SpringBoot와 MySQL을 연동하는 방법에 대해 알아보자.
MySQL을 연동하는데 필요한 의존성 추가
1 | |
application.yml
1 | |
- spring.datasource :
Database연동 관련 설정 정보- drive-class-name :
MySQL을 연동하고자 하므로com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver - url : 사용할 database url
- username : 데이터베이스 계정
- password : 계정 비밀번호
- drive-class-name :
- mybatis : Mapper 관련 설정
- type-aliases-package : mapper에서 사용할 클래스의 위치,
Mybatis에서alias를 만들어 준다. - mapper-locations : mapper 파일의 위치
- configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case : 테이블 필드명에 있는 underline(
_)을DAO에서camelCase로 변경해줌- ex) table:
user_id→ DAO :userId
- ex) table:
- type-aliases-package : mapper에서 사용할 클래스의 위치,
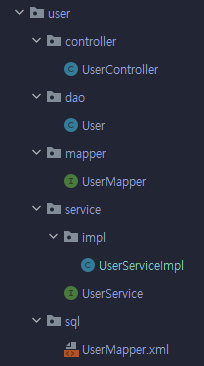
패키지 구조
- 패키지명 : com.spring.security.example
contoller
- UserController
1 | |
dao
- UserDAO
1 | |
- @Data :
@Getter,@Setter,@RequiredArgsConstructor,@ToString,@EqualsAndHashCode어노테이션을 자동으로 설정해주는Lombok어노테이션
mapper
- UserMapper
1 | |
- @Repository : 미리
MapperScan설정을 한 뒤 Dao 계층에서 생성된Bean을 서비스 계층에 주입함- 여러개의 매퍼를 사용하기 위해 Mapper scan이 필요하며 방법은 3가지임
XML기반 :<mybatis:scan/>엘리먼트 사용XML기반 : 스프링XML파일을 사용해서MapperScannerConfigurer를bean으로 등록JAVA기반 :@MapperScan어노테이션 사용
- 자세히 알고 싶다면 [Spring] @Mapper는 언제 사용하는걸까?
- 여러개의 매퍼를 사용하기 위해 Mapper scan이 필요하며 방법은 3가지임
- @Mapper :
xml의namespace를 통해Bean이 생성되어 서비스 계층에 삽입됨
service
- UserService
1 | |
- impl/UserServiceImpl
1 | |
sql
- UserMapper.xml
1 | |
- 해당
mapper의namespace가@Mapper어노테이션과 연결됨 - application.yml 파일의
mapper-locations설정으로 mapper 파일 등록됨 - application.yml 파일의
type-aliases-package의 설정으로resultType에서User를 사용 가능함
References
The difference between @Mapper and @Repository in spring boot